Are you confident in accurately reporting cryptocurrency earnings on your tax returns?
What Crypto Tax Forms Should I File?
Find which crypto tax forms you should file if you have crypto gains and losses. Get started with CoinTracker today.
February 21, 2020 · 5 min read

Form 8949, Schedule D, Schedule 1, Schedule A, Schedule B, Schedule C, Schedule E and Form 8275 are the most commonly used IRS crypto tax forms in the US. This post discusses when and how to file these tax forms easily using CoinTracker.
2020 Crypto Tax Forms - Quick Overview
- Form 8949 & Schedule D - to report sale of crypto assets, crypto futures income, crypto options income & crypto perpetual swap income.
- Schedule 1 - to report income from airdrops, forks, crypto wages and hobby income.
- Schedule A - to report crypto donations.
- Schedule B - to report DeFi income, crypto interest income and staking income.
- Schedule C - to report crypto mining income and business income earned in crypto.
- Schedule E - used as another option to report staking income.
- Form 8275 - to report additional disclosures (Optional).
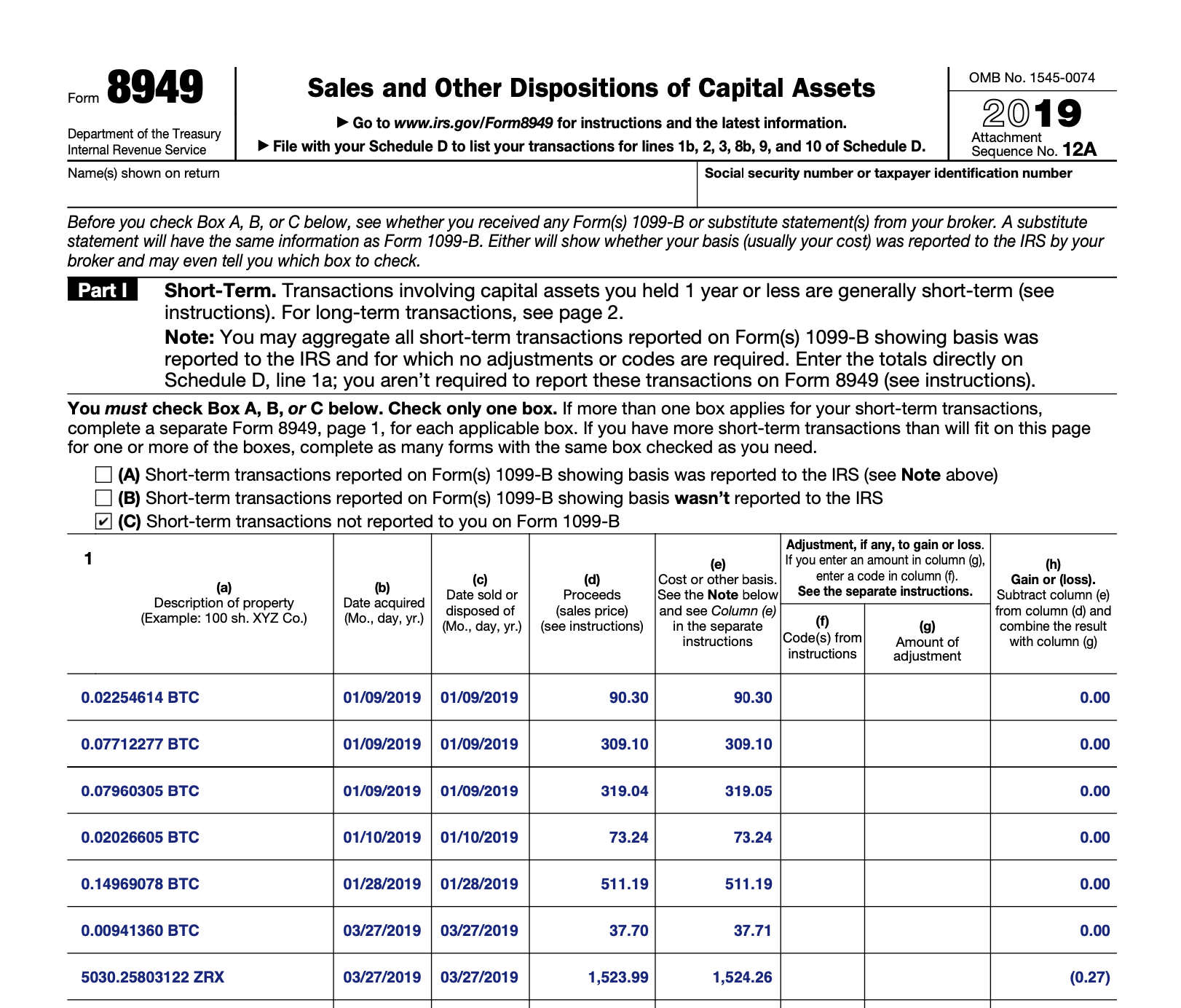
Form 8949 (Sales and Other Dispositions of Capital Assets)
Form 8949 is used to report your cryptocurrency capital gains and losses. The IRS uses information reported on this form to calculate your capital gains taxes.
To accurately fill out this form, you need to keep detailed records of the cost basis (how much you paid for each coin), market value of the coin at the time of sale and the how long you held each coin. This is an extremely tedious task to do manually. You can use CoinTracker to automate this process. Once you connect your exchanges and wallets to CoinTracker, you can generate a Form 8949 with all the transactions.
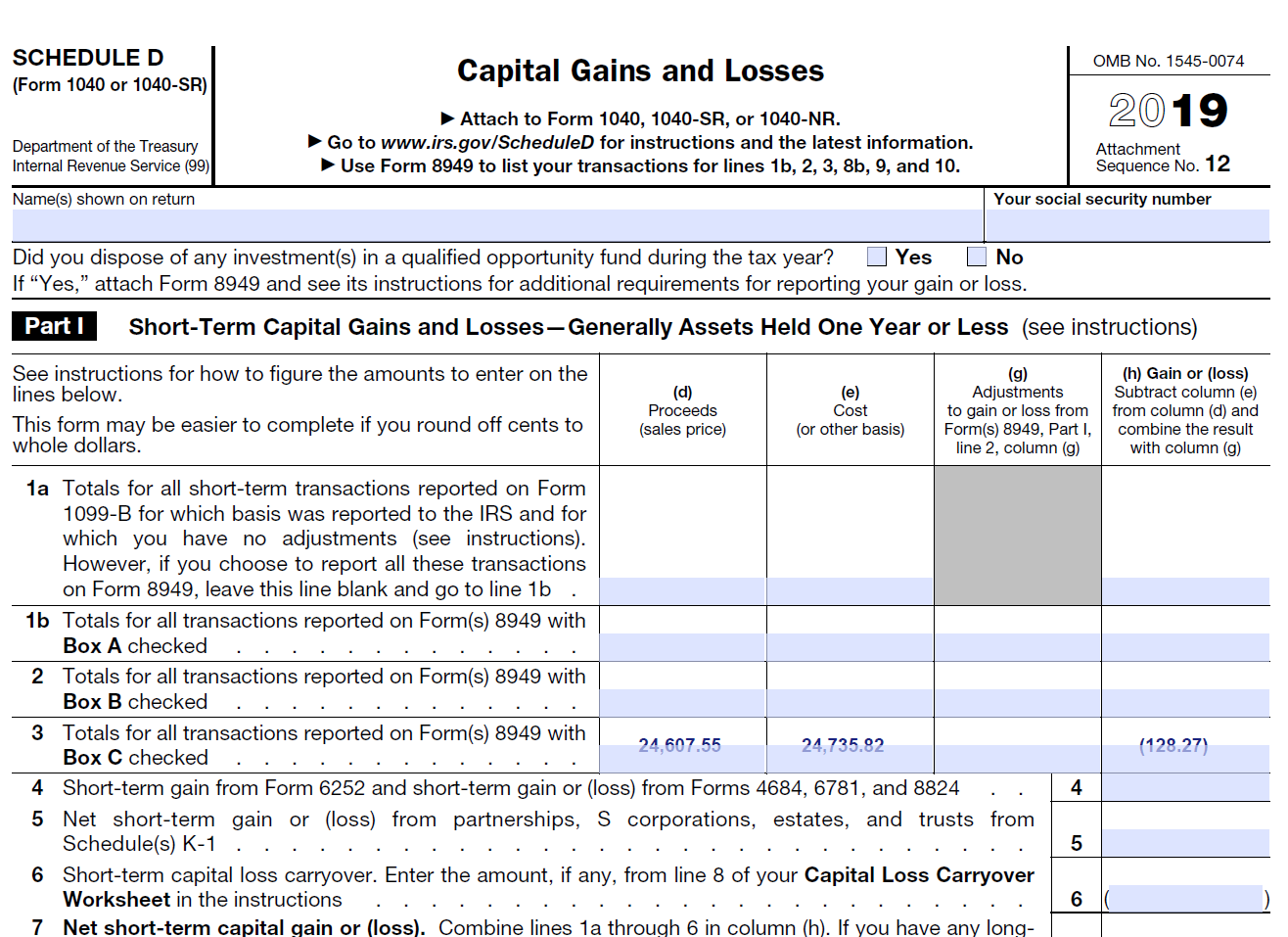
Schedule D (Capital Gains and Losses)
Schedule D summarizes what you reported on Form 8949. You can also produce this form on CoinTracker. This schedule will also show your stocks & security short-term and long-term capital gains & losses.
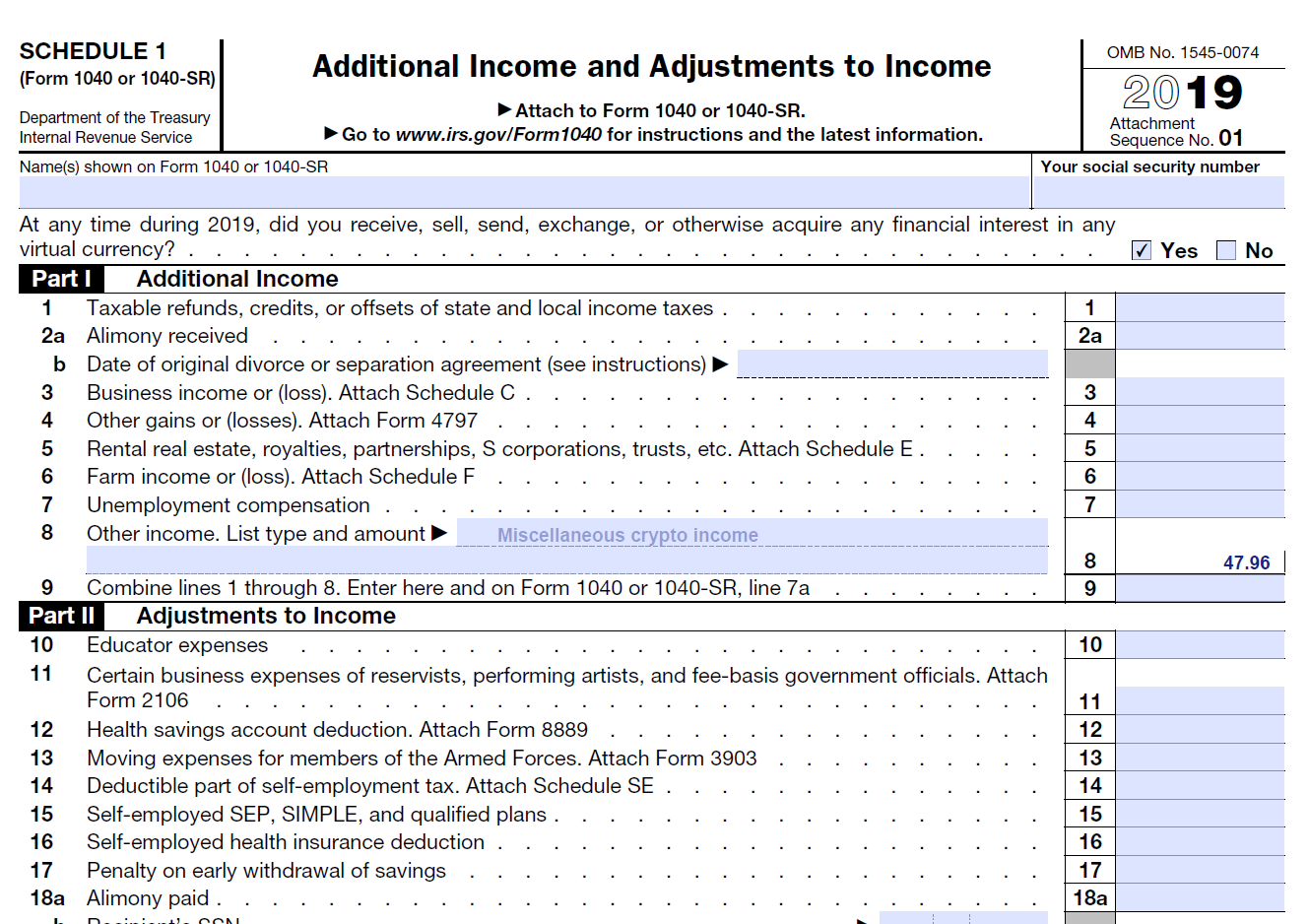
Schedule 1 (Additional Income and Adjustments to Income)
In 2019 tax year, on Schedule 1, you had to answer the question, “At any time during 2019, did you receive, sell, send, exchange, or otherwise acquire any financial interest in any virtual currency?”
Schedule 1, line 8 (Other Income) is used to report ordinary income coming from forks and airdrops and cryptocurrency received as wages.
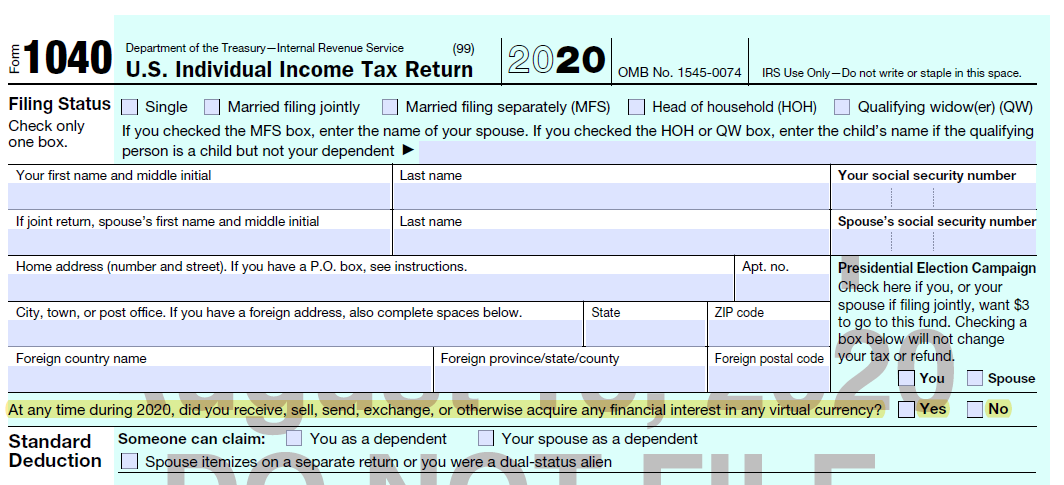
This infamous crypto tax question has been moved to the front of Form 1040 starting 2020 tax year
Schedule A (Itemized Deductions)
If you donate crypto assets to a qualified charity, the amount you are allowed to deduct would go on Schedule A line 12.

The amount you are eligible to deduct depends on how long you kept the asset. If you donate a cryptocurrency which you held for more than one year, you would get a deduction equivalent to the market value of the asset at the time of the donation. If you kept the asset for less than 12 months, you would get a deduction equivalent to the lesser of cost basis or market value, at the time of the donation.
If your deduction is more than $500, you will have to complete Form 8283 as well.
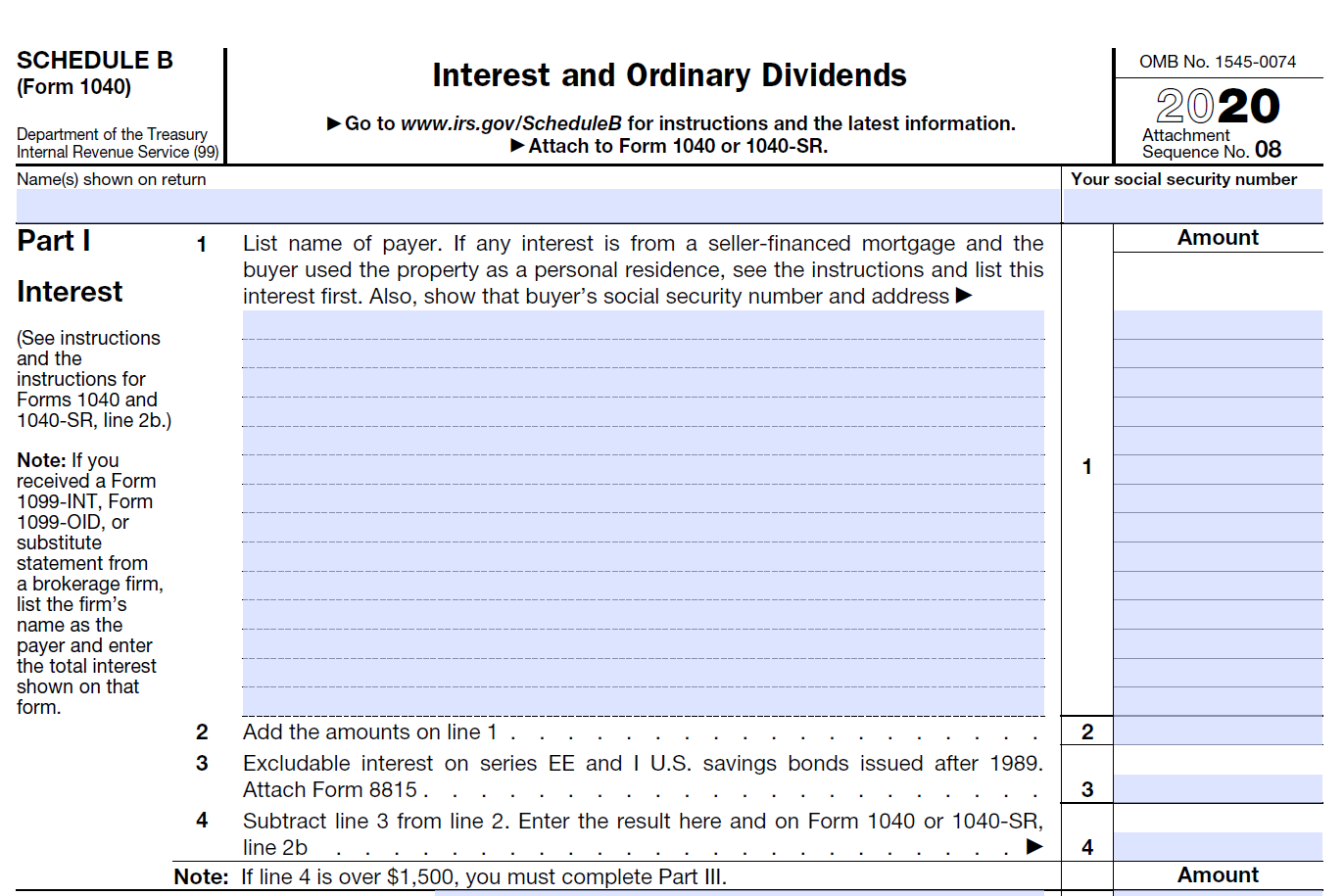
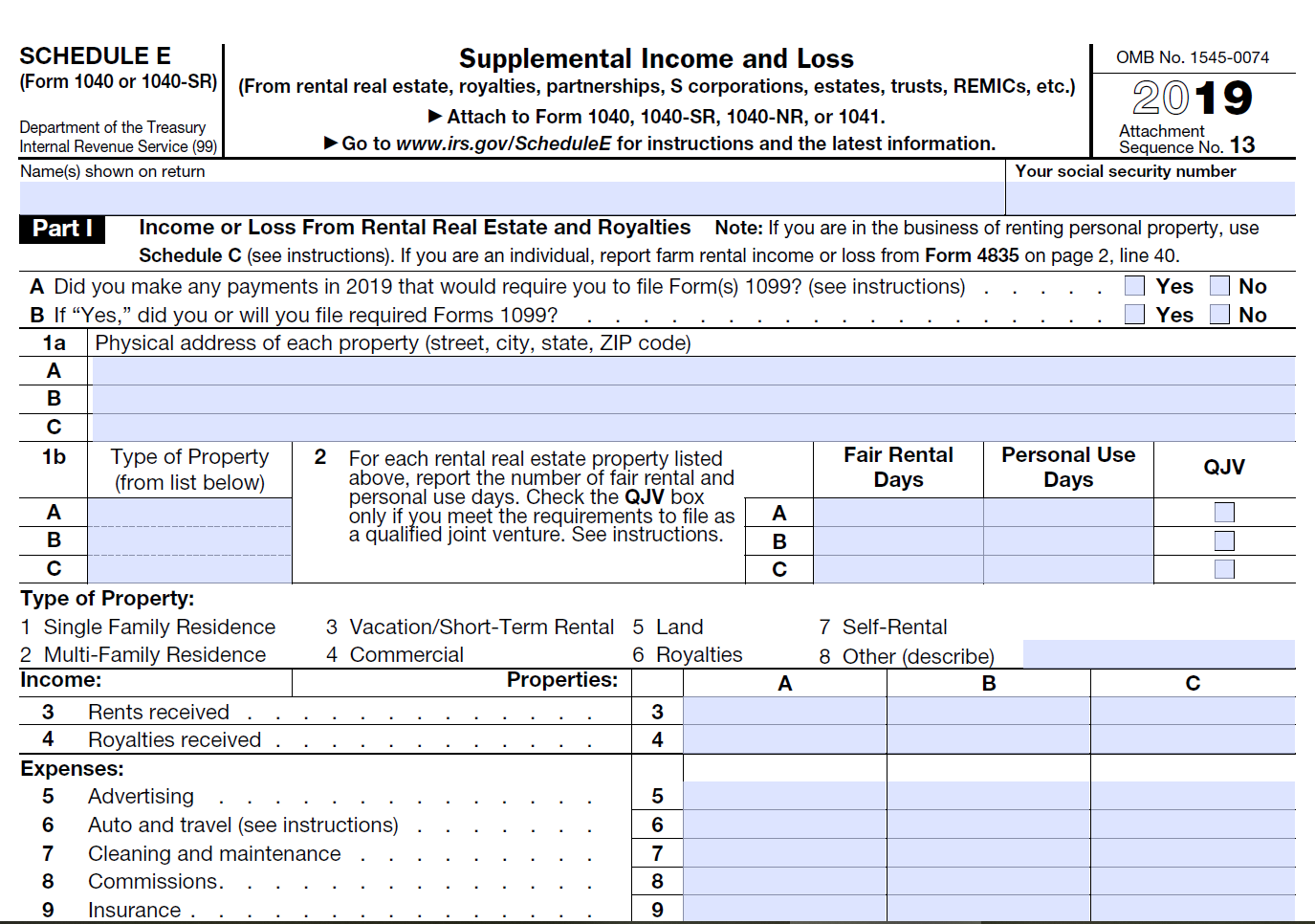
Schedule B (Interest and Ordinary Dividends) Or Schedule E (Supplemental Income and Loss)
Schedule B or E may be used to report income similar to staking rewards. The IRS has not come up with guidance related to how staking related income should be taxed. Some argue staking rewards are interest income while others believe that staking rewards should be reported as rental income (How Staking Tezos May Generate ‘Rental’ Income).
Interest income is reported on Schedule B and rental income is reported on schedule E.
Schedule C (Profit or Loss From Business)
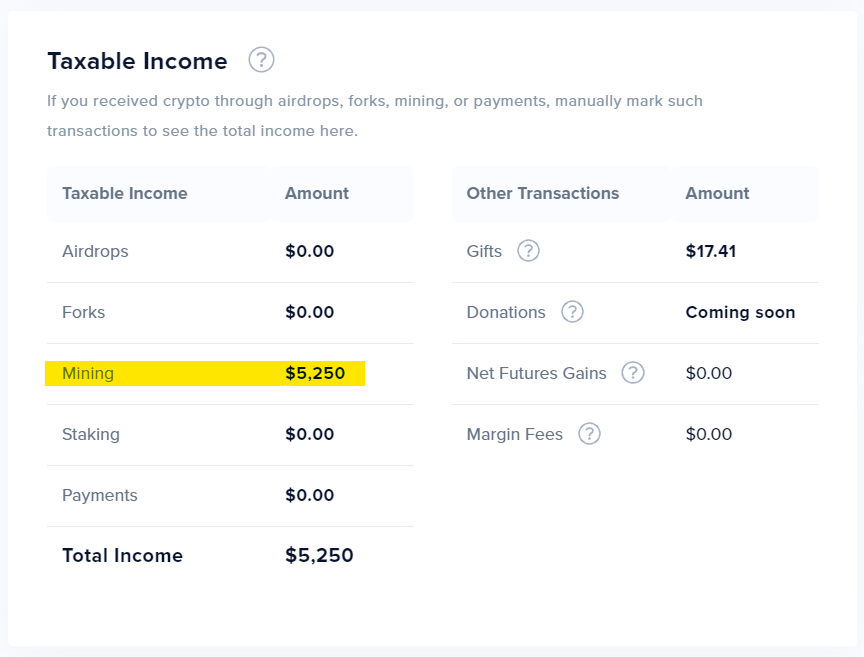
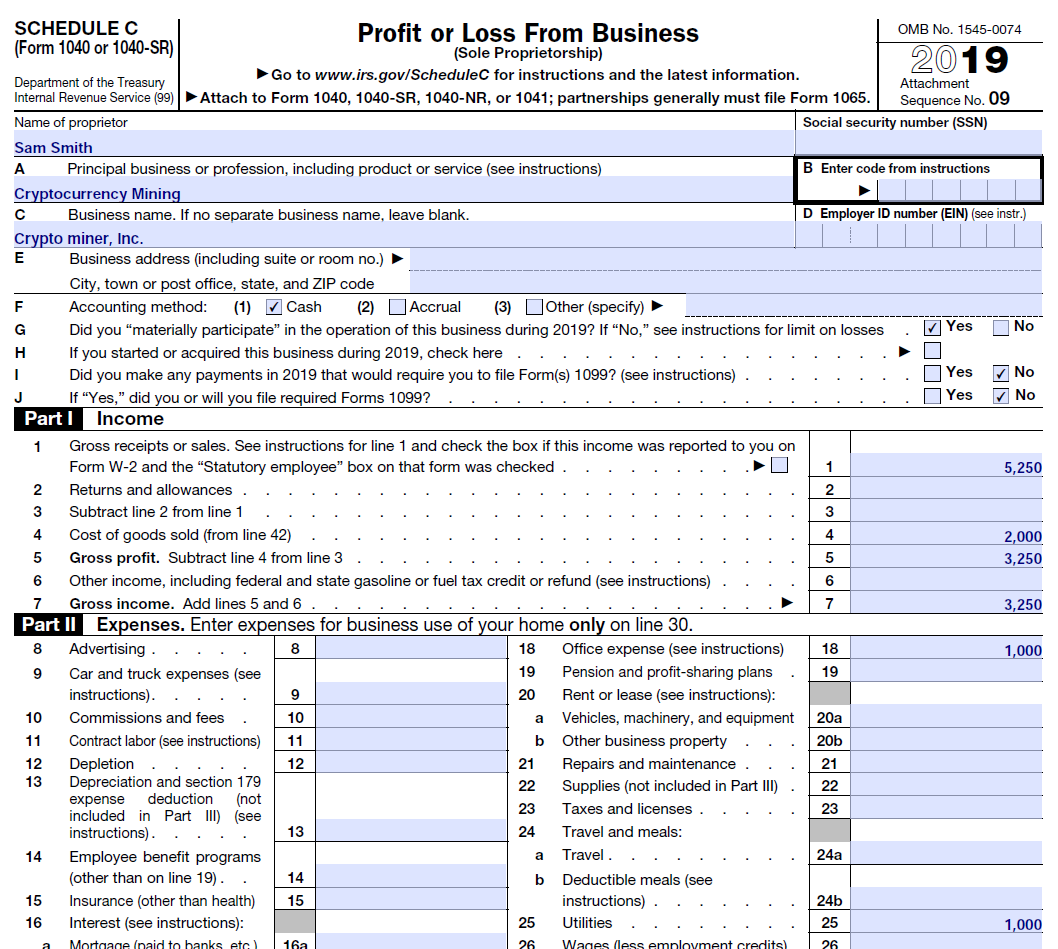
If you have a crypto mining operation which you carry out to make a profit (as opposed to a hobby), your mining income and related expenses would be reported on Schedule C.
Income to be reported on Schedule C, line 1 is the market value of the coins at the time you mined them. Some expenses you can use to offset mining income include mining equipment cost, utilities, internet, rent, etc. You will be taxed on the net income. CoinTracker Tax Center reports mining income to be reported on line 1 of Schedule C.
Form 8275 (Disclosure Statement)
Form 8275 should be used carefully. It is used to disclose positions that are not adequately disclosed on your tax return. Crypto tax space has a lot of general guidance but lacks specific guidance aimed at sophisticated transactions like futures, options, perpetual swaps, etc. When faced with sophisticated crypto transactions where you would take a position not directly addressed by the existing guidance, you can use this form to disclose the reasoning behind it. More disclosure is beneficial because it shows your good faith in reporting. Do not use this form without consulting with a tax attorney or a qualified crypto CPA.
Make sure to file the right crypto tax forms and also avoid these common crypto tax reporting pitfalls.
If you have any questions or comments about crypto taxes let us know on Twitter @CoinTracker.
CoinTracker integrates with 300+ cryptocurrency exchanges, 3,000+ blockchains, and makes bitcoin tax calculations and portfolio tracking simple.
Disclaimer: This post is informational only and is not intended as tax advice. For tax advice, please consult a tax professional.




